Monday to Saturday 9:00 am to 1:00 pm & 5:00 pm to 8:00 pm
Follow Us:
It is recommended that people with high numbers, all diabetics and people > 40 years of age get the retina checked at least once a year.
By putting some drops called “mydriatics” which dilate the pupils. The retina is the examined by an instrument called the “indirect ophthalmoscope".
Will someone need to accompany me for the checkup? – the pupillary dilatation can often cause significant blurring of vision for 3-4 hours. It is therefore recommended not to drive after the test. It is for the same reason that we often ask someone to accompany the patient for the test.(especially patients with already poor vision)
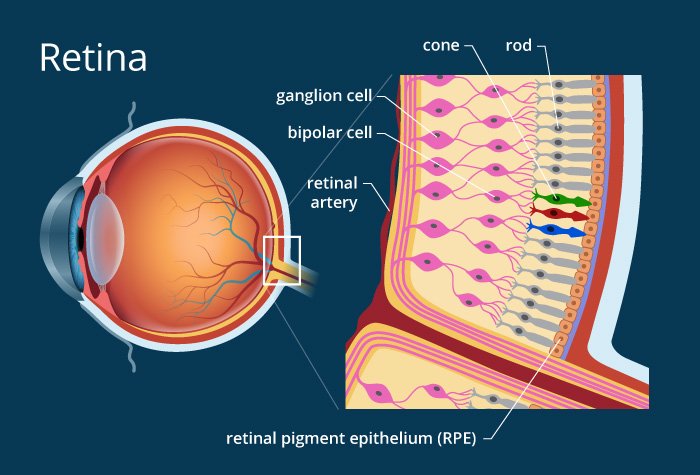
Diabetes affects the retinal capillaries and other blood vessels. The effects of these on the retina is termed diabetic retinopathy. Read More
It affects vision by producing swelling In the macula (called macular oedema) or by producing new blood vessels in the eye (neovascularization) which can then lead to vitreous haemorrhage or retinal detachment.
Yes it is preferable. People with numbers are more prone to develop weak areas (Lattice Degeneration) and retinal holes. They are also at higher risk of retinal detachment, especially if there is also a family history.
a sudden appearance of floaters, flashes that persist even after eye closure, curtain-like field loss and loss of vision.
No. retinal lasers are outpatient procedures (OPD).
No. but there is some discomfort during the procedures and few patients may complain of mild pain. Lasers are generally well tolerated. Read More
From one to many depending on the retinal disease and severity.
Yes. It is preferable to have an annual retinal check up as many eye changes including presbyopia ( reduced near vision) start after 49 years of age.
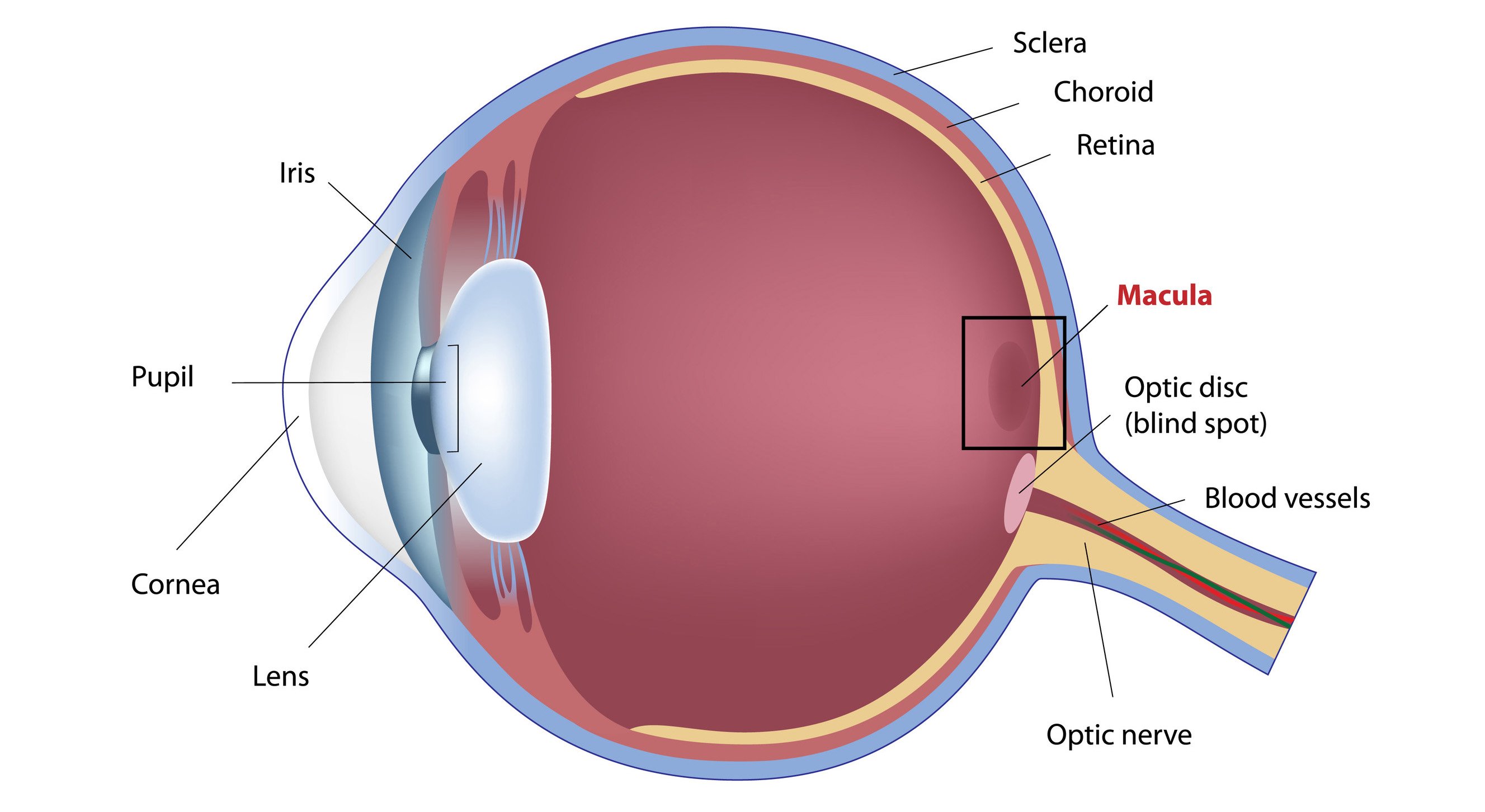
Age related macular degeneration (ARMD) refers degenerative changes occurring in the central retina characterized by deposition of a yellow material called Drusen.
ARMD is of 2 types: Dry or Wet
In wet ARMD, there is a collection of fluid or blood under the retina.
ARMD cannot be reversed. Its progress can only be slowed or arrested to some extent. Read More
VEGF is the short form of vascular endothelial growth factor. VEGF is an important chemical mediator for angiogenesis ( blood vessel formation) and permeability ( leakiness )
Avastin (Bevacizumab) is an anti-VEGF drug injected into the eye for treatment of diseases like WET ARMD and macular oedema due to diabetes or retinal vein occlusions. It is not FDA approved.
Accentrix ( ranibizumab) previously known as Lucentis is the FDA approved and current GOLD STANDARD for treatment of wet ARMD worldwide. It is also approved for macular oedema due to diabetes and vein occlusions. It belongs to the antiVEGF group.
Not really. The eye is made numb with the help of drops and the drug is injected into the eye via a microneedle. Read More
The injections per say take just a few minutes. The patient is immediately allowed to go home.
Yes definitely. Only care that needs to be taken is to Instill drops regularly.
Copyright © 2023 mumbai eye & retina clinic. | All Rights Reserved | Designed & Marketed by myEplatform®